Liaoning, China
| Province | Liáo nìng 辽宁 'distant better' |
| Short name | 辽 Liáo |
| Capital | Shenyang |
| Population | 42.591 million (3.01%) [14th] comparison table |
| Area | 146,000 km2 [56,371 mile2] (1.52%) [21st] |
| GDP | 58,967 (10.04%) [17th] |
| Neighbors | Jilin Hebei Inner Mongolia North Korea |
| Others | or just click on the map |
Liaoning is the southernmost of the Manchurian provinces and holds a vital strategic position in northern China. One of the main lines of the Great Wall (the Han rather than the Ming version) snakes itself through the province. The province has rapidly developed from Song dynasty times onwards.
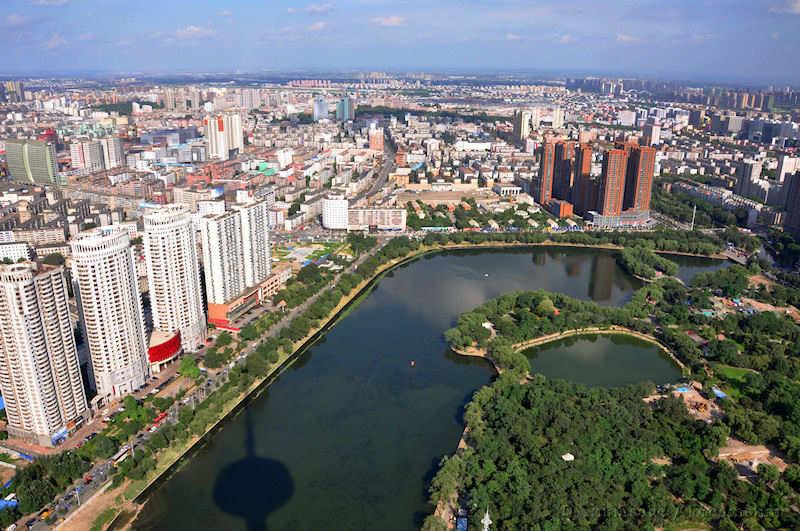
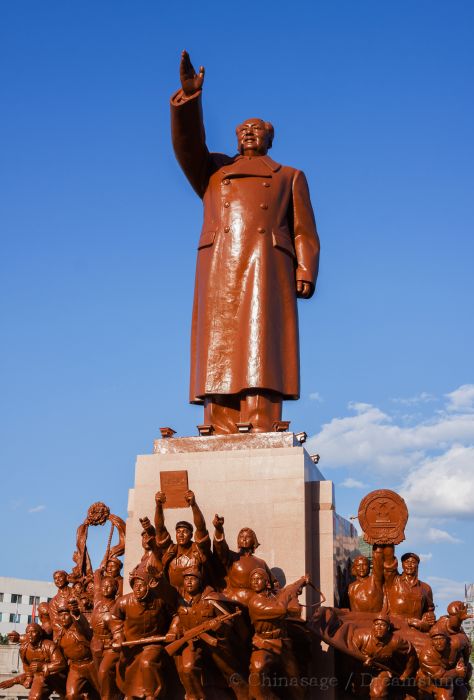


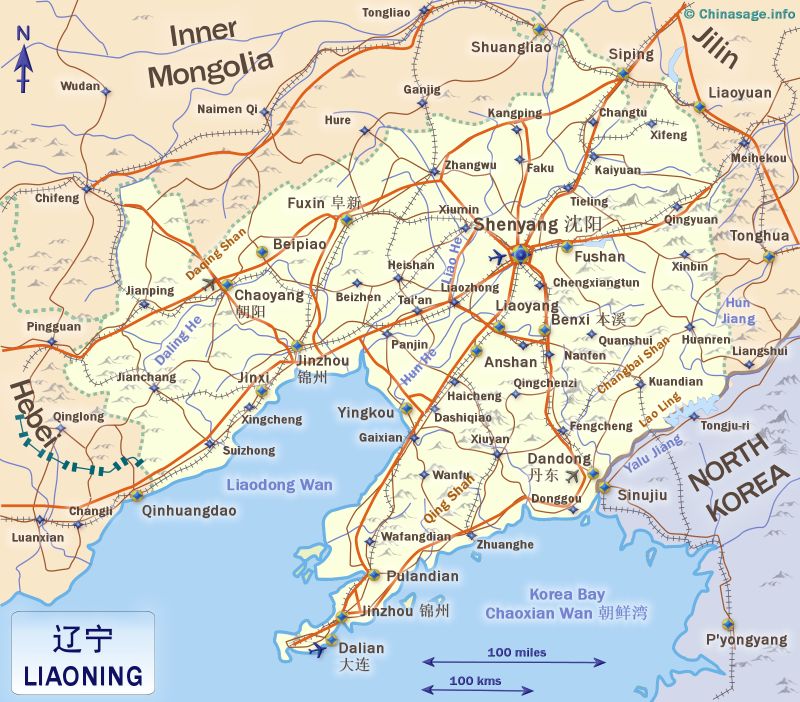
Shenyang
Shenyang was the Manchu capital (‘Mukden’ its Manchu name is still sometimes used) and has many historical sites within the large industrial city. By some measures Shenyang is amongst the most densely populated cities in the world. Emphasizing the importance of railways to the city and the area's development, Shenyang has a railway museum. There is a Manchu palace which is a small scale replica of the Forbidden City completed in 1636. Nearby are tombs of the Manchu kings (the East and North tombs) before they founded the Qing dynasty in China. The city is famous for a colossal epoxy statue of Mao Zedong standing in Zhongshan Square. The Xiuyuan district has Manchu traditional housing and also a museum of Manchu history and culture.
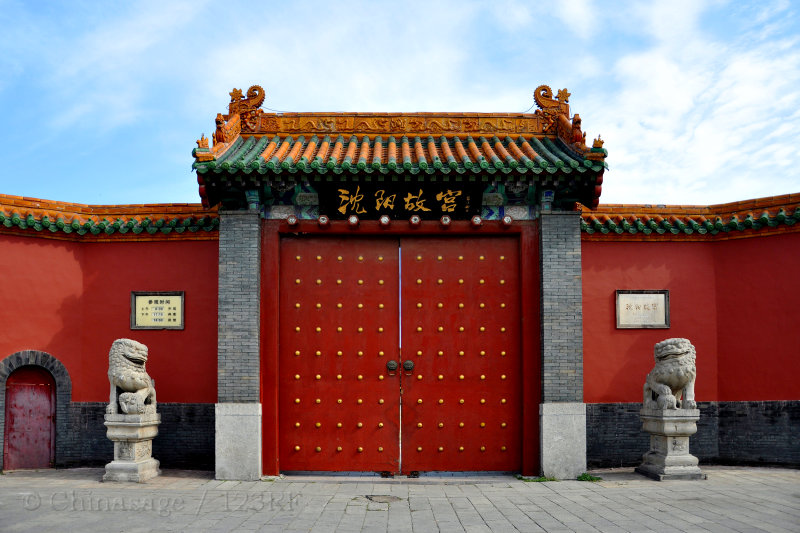

Places to visit in Liaoning
Jinzhou on the railway line west to Hubei is famous for its dinosaur fossils. Anshan is an industrial city producing vast amounts of iron and steel. Nearby is the scenic spot of Qianshan ➚ Thousand lotus mountain which has many pavilions and temples among pine trees. The industrial city of Fushun has coal deposits nearby and is known for cement and petrochemical industries. Many of the large cities have a heavy industrial feel, emphasized by the flat terrain of the north-east plain.
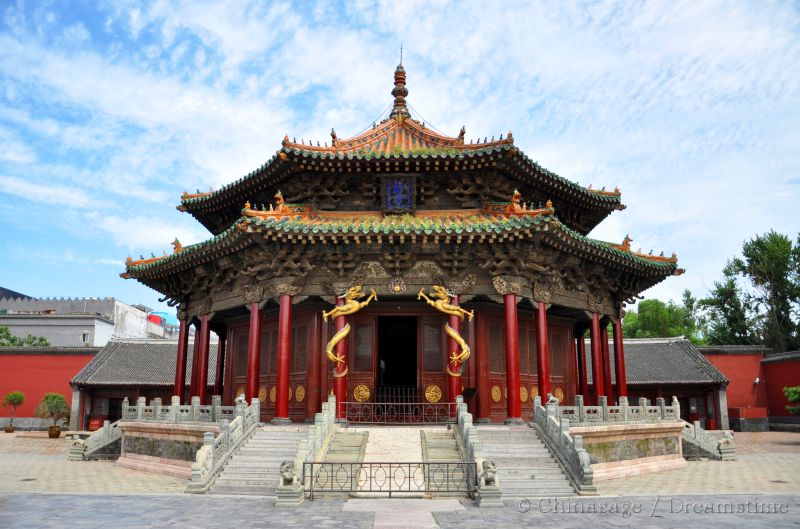

Dalian (also known as Dairen) is a major port for the industrial output of the north-eastern provinces rivaling Tianjin and often compared to Shanghai for its cosmopolitan and entrepreneurial feel. Laotieshan Nature Park ➚ is at the tip of the peninsula; while Bingyu Valley ➚ on the south side of the peninsula has fine scenery. The port of Lushun can be visited but only with a permit because it is an active naval base. There are seaside resorts scattered along the Liaodong Sea coast including Xingcheng ➚ with a Ming architectural style and Jinshitan ➚ beach which is a popular tourist spot. Liaoning's rocky coast has many fine beaches and fish restaurants.
Near to Yixian is the Fengguo Temple ➚ built a thousand years ago, and there is the Ancient City of Tayingzi ➚ close to Fuxin. Benxi has dramatic scenic caves. Close by is the Tiecha Mountain ➚ sacred to Daoists. Dandong stands close to the border with North Korea and has a portion ➚ of the restored Great Wall going up the mountain. Close by are the scenic Dagushan mountains as well as the Wulongbei Hot Springs. Many ethnic Korean people live in the area close to the border with North Korea.

Liaoning History
The mountainous peninsula of Liaoning was the scene of a dispute between Russia and Japan in the early 19th century. The city of Lushun lies at its tip, and was known as ‘Port Arthur’ by westerners as the British named it after a naval officer William Arthur ➚. Port Arthur was overrun in November 1894 by the Japanese, then in 1895 Russia pushed out the Japanese and took over the area. The Battle of Port Arthur on February 9th 1904 between Japan and Russia resulted in Japanese victory. Rapid railway and industrial development followed the Japanese occupation in 1895; it remained under Japanese influence as part of Manchuria/Manchuguo until 1945. The ‘Mukden Incident ➚’ of 1931 was a ruse to validate further Japanese control. Many people moved from overcrowded Shandong into the area in the period 1870-1950 – the ‘Chuang Guandong ➚’.
There are now plans ➚ to construct a huge 76 miles [123 kms] bridge and tunnel across the shallow Bohai Sea to Shandong.
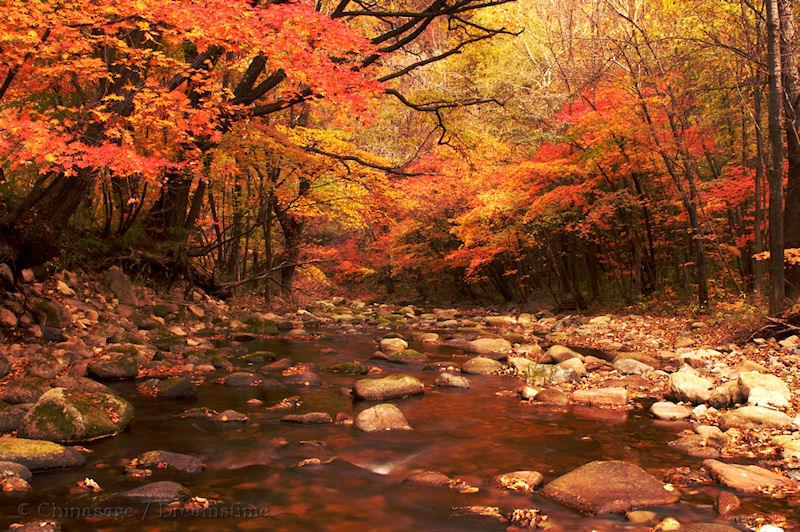

Liaoning Geography
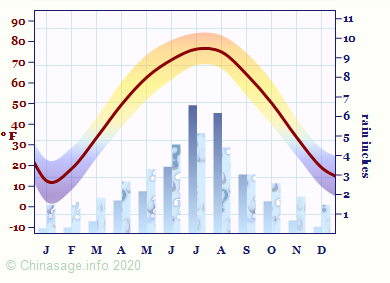
The North China plain has brief warm summers and long cold winters giving limited scope for food production except in the coastal area. It is famous for its vast apple and pear orchards. Liaoning has a wide variety of natural resources: coal, oil shale, iron, lead and even uranium. It has 25% of China's iron ore reserves and second only to Shanxi in coal deposits. Manchu people form a significant but small minority and there are also Korean people close to the Korean border.
Airports
The airport has 1 terminal and is located 12.4 miles (20.0 kms) from Shenyang. Live Flight information ➚, rank in China 25
International Links to :Japan Korea
See map of location Shenyang Taoxian International Airport
The airport has 1 terminal and is located 5.0 miles (8.0 kms) from Dalian. Live Flight information ➚, Airport information ➚, rank in China 23
International Links to :Japan Korea Germany
See map of location Dalian Zhoushuizi International Airport
Google map of Liaoning
Bing map of Liaoning ➚
Show Bing Map ➚
Liaoning Climate
| Major Cities | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Anshan | 鞍山 | 1,647,000 |
| Benxi | 本溪 | 1,176,490 |
| Chaoyang | 朝阳 | 537,800 |
| Dalian | 大连 | 5,736,383 |
| Dandong | 丹东 | 659,400 |
| Fushun | 抚顺 | 1,307,200 |
| Fuxin | 阜新 | 759,100 |
| Huludao | 葫芦岛 | 724,800 |
| Jinzhou | 锦州 | 604,269 |
| Liaoyang | 辽阳 | 793,700 |
| Panjin | 盘锦 | 846,500 |
| Shenyang | 沈阳 | 7,885,142 |
| Tieling | 铁岭 | 434,799 |
| Wafangdian | 瓦房店 | 250,591 |
| Yingkou | 营口 | 848,100 |
Book: China : Eyewitness Travel: Dorling Kindersley: 2012 pp. 432-445
Book: Insight Guides: China: APA publications: 1994 pp. 187-190
Book: Lonely Planet: China: 1988 pp. 554-568
Book: Modern China: A companion to a rising power: Graham Hutchings:… pp. 278-282
Book: Nagel's Encyclopedia guide: China: Nagel: 1978 pp. 1422-1427
Web page: Liaoning (wiki) ➚
Web page: Liaoning Travel Guide: Map: History: Sightseeing: Ethnic Minority: Climate ➚
Web page: Map of Liaoning Province: China ➚
City populations for 2012, Province statistics National Bureau of Statistics 2014