Heilongjiang, China
| Province | Hēi lóng jiāng 黑龙江 'black dragon river' |
| Short name | 黑 Hēi |
| Capital | Harbin |
| Population | 31.85 million (2.25%) [20th] comparison table |
| Area | 469,000 km2 [181,081 mile2] (4.89%) [6th] |
| GDP | 43,009 (5.48%) [32nd] |
| Neighbors | Russia Jilin Inner Mongolia |
| Others | or just click on the map |
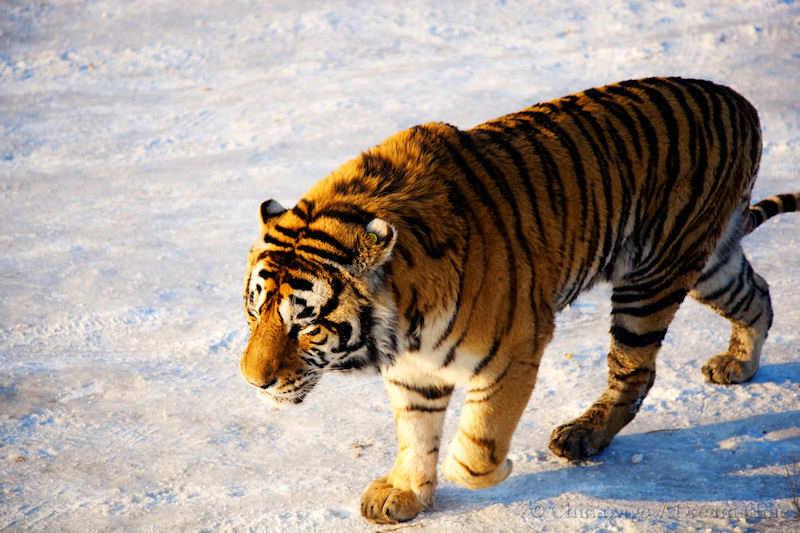


Heilongjiang is named after the ‘Black Dragon River’ that forms much of its eastern border with Russia (the Russians call the river ‘Amur’). The province shares its harsh, cold winters with Russia too.
Heilongjiang History
The province was part of the Korean Balhae Kingdom ➚ at the time of the Tang dynasty. This kingdom went on to be ruled by the Jurchen Jin Dynasty. It only became an integral part of China in the Qing (Manchu) dynasty. At this time it was only sparsely populated and not seen as strategically or economically important. As part of Manchuria it was invaded and industrialized by the Japanese in the 1930s, for it has extensive timber, coal, iron and oil deposits. The rural border regions have people of Manchu; Hui; Korean; Oroqen and Mongolian origin.
It was the building of the Trans-Siberian Railway through to Vladivostok that led to the rapid urban development of Heilongjiang, particularly at Harbin. Russian investment has remained an important spur to development in the province.
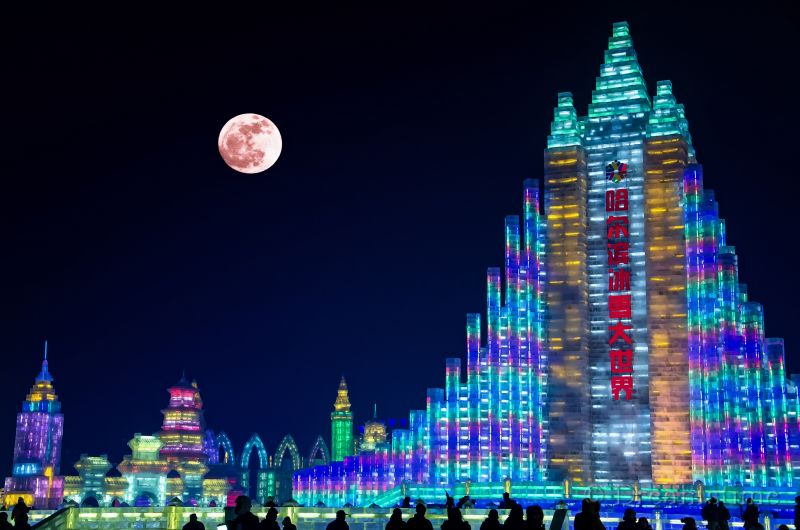

Harbin
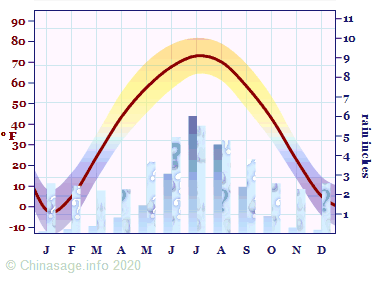
Harbin has a famous ice sculpture fair at Zhaolin Park ➚ from January to March, reflecting the long, cold winters (typically -22 ° F [-30 ° C]). It gets so cold that fruit and milk are sold in frozen form. Lanterns made out of ice feature at the Chinese New Year festival. To complete the icy theme there are ski slopes nearby at Shangzhi ➚.
Harbin, whose name means ‘Place for drying fish nets’ is a relatively modern city, only a hundred years ago it was a fishing village on the Songhua River. The strong Russian involvement in the early twentieth century can be seen in the local architecture including the onion dome of St. Sofia. It has recently built an impressive Opera House ➚ of very modern design. The city has been laid out with 13 public parks.

Places to visit in Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang has impressive mountain scenery and its fringes are covered with dense pine forests. A Siberian Tiger Reserve ➚ is located near to Harbin. An area with important industrial history is the famous Daqing oilfield which was strategic during the Mao era when China was isolated and had to rely on its own scarce sources of oil.
Mirror Lake ➚ (Jingpo) is a volcanic lake (22,239 acres [90 sq kms]) south-west of Mudanjiang set amongst the forests. It is a popular resort particularly for fishermen. Qiqihar is an old industrial town while nearby is the Zhalong Nature Reserve ➚ that attracts many birds, particularly on migration, and is the home of rare red-crowned ➚ and white-naped ➚ cranes. Wudalianchi ➚ (meaning Five inter-linked lakes) north of Bei'an is another popular scenic spot amid one of China's few active volcanic areas at Dixia Senlin. Yichun ➚ is a historic forestry town with many old adobe buildings.

Geography
The Songhua River ➚ has been subject to high levels of pollution as it flows through many industrial cities picking up associated industrial and domestic waste. Extensive pasture lands make Heilongjiang the most important province for dairy products, it is also produces a large amount of grain and soybean.
Airports
The airport has 2 terminals and is located 20.5 miles (33.0 kms) from Harbin. Live Flight information ➚, rank in China 22
International Links to :Korea Russia
See map of location Harbin Taiping International Airport
Universities
Harbin Institute of Technology 哈尔滨工业大学
The Harbin Institute of Technology is the leading university in northeastern China. It is actually split over three campuses spread over three provinces: Weihai in Shandong; Shenzhen in Guangdong and Harbin in Heilongjiang. It concentrates on space technology; military technology and general engineering. The Harbin campus has some hints to its history of Russian influence.. Undergraduates: 25002, Postgraduates: 12710, International students: 1584, GP World ranking 291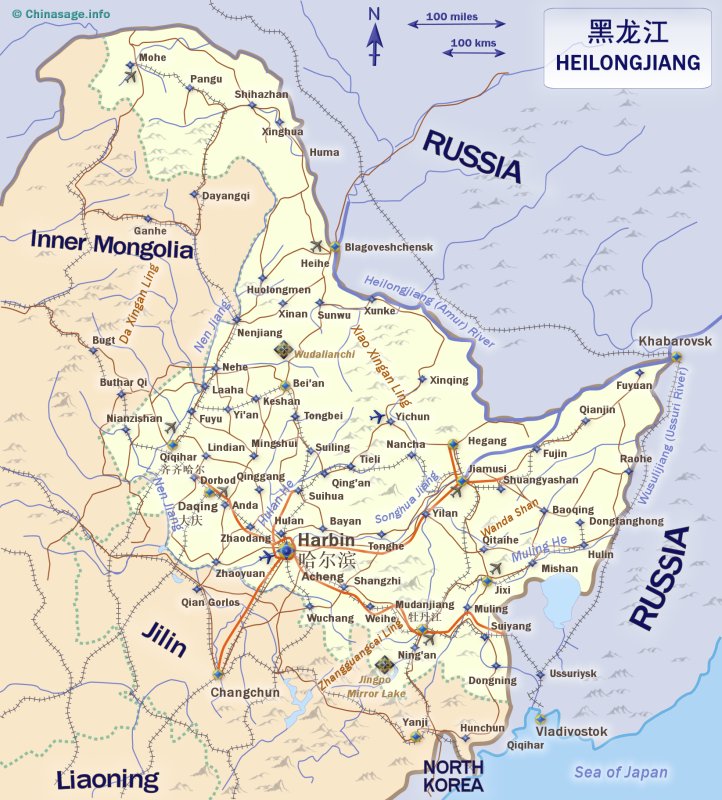
Google map of Heilongjiang
Bing map of Heilongjiang ➚
Show Bing Map ➚
Heilongjiang Climate
| Major Cities | Population | |
|---|---|---|
| Bei'an | 北安 | 436,444 |
| Daqing | 大庆 | 1,574,389 |
| Harbin | 哈尔滨 | 6,976,136 |
| Hegang | 鹤岗 | 690,000 |
| Jiamusi | 佳木斯 | 726,622 |
| Jixi | 鸡西 | 580,000 |
| Mudanjiang | 牡丹江 | 930,105 |
| Qiqihar | 齐齐哈尔 | 1,350,434 |
| Qitaihe | 七台河 | 620,935 |
| Shuangyashan | 双鸭山 | 507,257 |
| Suihua | 绥化 | 428,795 |
| Yichun | 伊春 | 598,000 |
Web page: :: XINHUANET :: ➚
Book: 60 Scenic Wonders in China: New World Press: 1980 pp. 226-228
Book: China : Eyewitness Travel: Dorling Kindersley: 2012 pp. 450-455
Book: Insight Guides: China: APA publications: 1994 pp. 189-192
Book: Lonely Planet: China: 1988 pp. 578-590
Book: Modern China: A companion to a rising power: Graham Hutchings:… pp. 187-188
Web page: Heilongjiang (wikitravel) ➚
Web page: Map of Helongjiang Province and travel guide ➚
City populations for 2012, Province statistics National Bureau of Statistics 2014