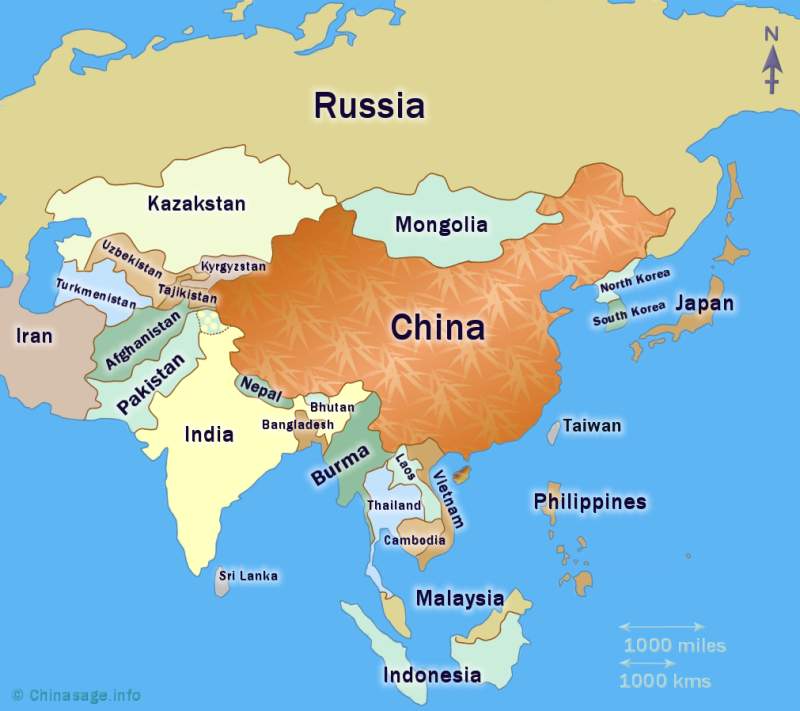
China's neighboring countries
This page looks at all of the 14 neighboring countries that have a land border with China. The important island neighbor/province of Taiwan has its own page as well as the islands of Japan. The history of Chinese relations with Korea also has its own page. The sea to the south of China is an area of disputed ownership and this is also fully described separately. You can use the map above to show information in a popup, you can then click on ‘Details’ to go to a description of the country.
China together with Russia has the largest number of land borders with neighboring countries - a total of 14. They are (running anti-clockwise from the East) : Korea (North), Russia, Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Laos and Vietnam. China's borders have changed many times over the centuries and relations with neighbors reveals a complex history. It was only in the nineteenth century that China's borders were fixed and the concept of China as a nation state developed. Up until the 19th century the Chinese considered themselves rulers of ‘all under heaven’ with a unique role, the emperor was the Son of Heaven for all mankind not just Chinese people. China was at the center and peoples were regarded as increasingly savage and barbaric the further out they lived. You can click on a country in the map to go to a description of the country.
Russia 俄罗斯 (Eluosi)
Population 144 million Area 17,098,242 sqkms GDP $8,184Up until the 16th century Russia was a small European state centered around the western coast of the Baltic Sea. After the fall of the Mongolian Sibir Khanate in 1581 the Russian Empire rapidly expanded by swallowing up numerous small kingdoms in Central and Eastern Asia.
The Great Game ➚ was played out in Central Asia between Russia and the U.K. (1813-1907). Britain wished to protect its important interests in India (The Jewel in the Crown ➚) by thwarting the further southern expansion of Russia. This led to British wars over Afghanistan (1839-42; 1878-1880 and 1919). Britain took over control of Tibet in 1902 to prevent Russian influence building there. Britain also encouraged her then ally Japan to block Russian advancement in Korea and Manchuria.
The Eastern border of China with Russia has always been more contentious. The Treaty of Nerchinsk 1689 gave China control over the productive land east of the Heilongjiang (Amur) River. Increasing Russian military power forced China to reverse this at the Treaty of Aigun ➚ in 1858 which was at the time of the ruinous Opium Wars with Britain. Russia quickly established a port at Vladivostok in 1861, giving her access to the north Pacific. Russia wanted a railway link to their new port and this required building the Trans-Siberian Railway through Chinese Manchuria. At the same time the Russia-China border to the north-west was the scene of incursions by Chinese bandits. Russia retaliated by invading the Ili valley ➚ around Yiling, Xinjiang (1860-61).
The Sino-Japanese War (1894-95) gave Russia further opportunities to squeeze concessions out of China Li Hongzhang ➚ signed the Sino-Russian Treaty in 1896 ceding Russia the rights to build the Trans-Siberian railway through Chinese territory. Russia also took control of Port Arthur (now Lushun) in Liaoning (1898) controlling the Yellow Sea route to Tianjin. After the Russian revolution in 1917 the situation was transformed. The USSR now supported both the Communists and Nationalists in China in their rebellion against the Qing regime. When a Peoples' Republic was founded in Mongolia in 1924 Russian influence to the north of China strengthened. It was only after the Long March that Russian support fell solidly behind the Communists rather than the Chiang Kaishek's Nationalists . When Japan surrendered on 6th August 1945, Stalin sent Russian troops into Manchuria. This proved pivotal to the outcome of the following Civil War as Russians helped the Communists take over the area and pick up discarded Japanese military equipment. After the foundation of the People's Republic in October 1949 Russian technical, military and economic support flowed into China. A number of large scale engineering projects began including the Sanmenxia Dam ➚, Shanxi on the Yellow River in 1951. A secret deal gave China access to supplies of uranium and Russia initially helped develop the first Chinese atomic bomb ➚.
In the late 1950s and early 1960s the ‘Sino-Soviet Split’ first cooled relations and then transformed them into outright hostility. There was personal animosity between Mao and Khrushchev ➚ as they held different views on how Communism should develop. In 1969 the Battle of Damansky Island ➚ on the Ussuri River tensions turned into armed conflict, if only for 90 minutes. It was the intervention of Ho Chi Minh ➚ of Vietnam that helped calm tensions. In the 1970s Russia supported hostile regimes to China in Vietnam, Laos and built up offensive capability along its long border with China particularly in Mongolia. China built extensive military defenses on Hainan island as China feared invasion from Vietnam, and it was only with the break-up of the USSR in the 1990s that tensions have eased.
See also Russia (Wikipedia) ➚
Image by Fir0002 ➚ available under a Creative Commons license ➚
Mongolia 蒙古 (Menggu)
Population 3 million Area 1,566,000 sqkms GDP $9,293Mongolia takes a large bite out of the northern China. The exact border with China is still a matter of dispute as the border passes through open grassland and desert with no convenient geographical feature to mark a boundary. Over the last few thousand years China has had troubled relations with the Mongol people to the north and especially the Mongol Conquests under Genghiz Khan. Although mainly flat desert in the west the eastern portion is a land of mountains and rivers.
It was an integral part of China in Mongol (Yuan) and Qing dynasty times. The division of Mongolia as a separate sovereign nation is a little accident of history. After the fall of the Qing (Manchu) dynasty in 1912 Outer Mongolia declared itself independent. Then came the Russian Communist revolution of 1917 and the Russians supported revolution in Outer Mongolia and it became a Communist state in 1924. As part of a deal for support in China's war against Japan (1937-45), China acknowledged Russian control of Mongolia. It remained allied with Russia through the years of poor Sino-Soviet relations and served as the base for many Russian military outposts. With the break-up of the USSR, Mongolia took the route to independence and market reform in 1992.
Although a large country in land area it is sparsely populated. Many Mongolian are still nomadic herdsmen like their ancestors centuries ago. There are more ethnic Mongolians in northern China, particularly in Inner Mongolia than in Mongolia itself.
See also Mongolia (Wikipedia) ➚
Korea 朝鲜 (Chaoxian)
South Korea: Population 25 million Area 120,540 sqkms GDP $1,800 North Korea: Population 51 million Area 100,210 sqkms GDP $36,601China has seen the Korean people as part of the Chinese family for centuries. Korea had been a vassal state at various times from Han dynasty all the way through to the Qing dynasty. Korea's relations with China have been important for centuries particularly in the last hundred years and so we have dedicated a whole section to Chinese relations with Korea.
See also Korea (Wikipedia) ➚
Vietnam 越南 ( Yuè nán)
Population 91 million Area 338,698 sqkms GDP $5,621The modern state of Vietnam is a relatively recent invention after the break-up of French Indo-China. Vietnam has a vague border with Guangxi and Yunnan provinces running across mountain ranges. Northern Vietnam came under Han dynasty influence 2,000 years ago. Over the following centuries Annam (of which Vietnam formed a part) was seen as a ‘little brother ➚’ of China.
When the Qing dynasty came under attack from foreign powers in the Opium Wars France took advantage and made Vietnam part of her French Indo-China Empire in 1885. After the French were ejected from Indo-China in 1954 as a result of internal revolts it soon became prey to the political ambitions of USSR, US and China. The US military intervened in 1955 to support the beleaguered southern Vietnamese government under the pretext of preventing Communist overthrow from northern Vietnam. Initially both China and Russia supported the Viet Minh in the North. Their leader Ho Chi Minh spoke good Chinese and had good contacts with the Chinese Communist leadership. After the Sino-Soviet ➚ split, China switched its support to the Khmer Rouge ➚ in Cambodia (Kampuchea) rather than Vietnam (even though Cambodia does not have a land border with China), Cambodia then became China's key ally in south-east Asia. China undertook a punitive, short invasion of Vietnam in 1979 which is judged a failure as it met stiff resistance.
With the break-up of the USSR in 1991 Vietnam became an independent sovereign state with better relations with China and has seem burgeoning bilateral trade. There remain causes of tension with China including disputed territorial claims over the Spratly Islands. China maintains territorial claims to much of the South China Sea which should logically belong to Vietnam.
See also Vietnam (Wikipedia) ➚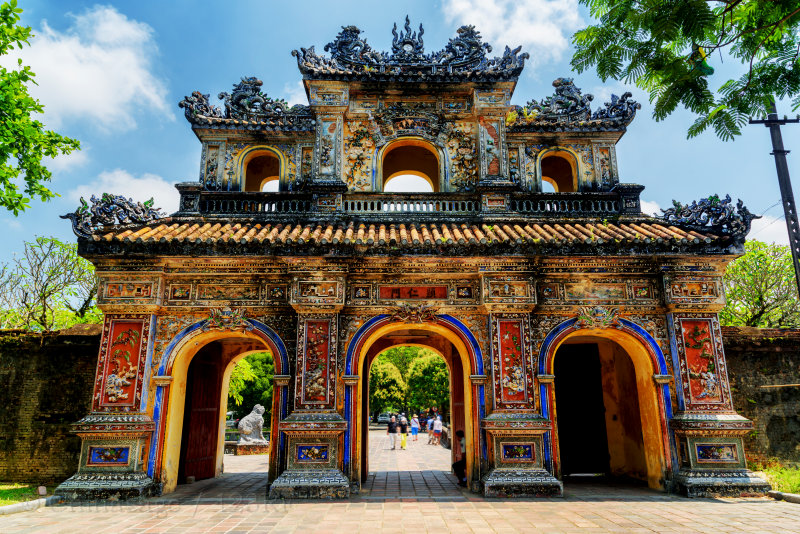
Laos 老挝 (Laowo)
Population 7 million Area 236,800 sqkms GDP $3,100Yunnan province's border with Laos is short (only 200 miles [322 kms]) and hidden in the mountains. Many indigenous tribes in Yunnan have historical links with related peoples just over the border. Fa Ngum ➚ founded the Lan Xang kingdom in the 14th century. Theravada Buddhism remains the dominant religion and provides the cultural backdrop. In the mid 18th century the kingdom of Laos suffered incursions from neighboring Burma.
During the Qing dynasty the Black Flag Army ➚ (Chinese rebels) invaded Laos and Vietnam. This soon escalated into the Sino-French War ➚ of 1884. Laos shared a similar fate to Vietnam, it was annexed by France during the years of dwindling Qing power after the Opium Wars. On the break-up of French Indo-China in 1954, Civil War broke out and the country became embroiled in the Vietnam/Cambodia Wars. In 1975 Pathet Lao ➚ with Russian support founded the Lao People's Democratic Republic. For this period the border with China was closed. It has only been since 1989 that relations with China have normalized. Laos remains a poor land-locked country. Road links with Yunnan have recently increased trade with China.
See also Laos (Wikipedia) ➚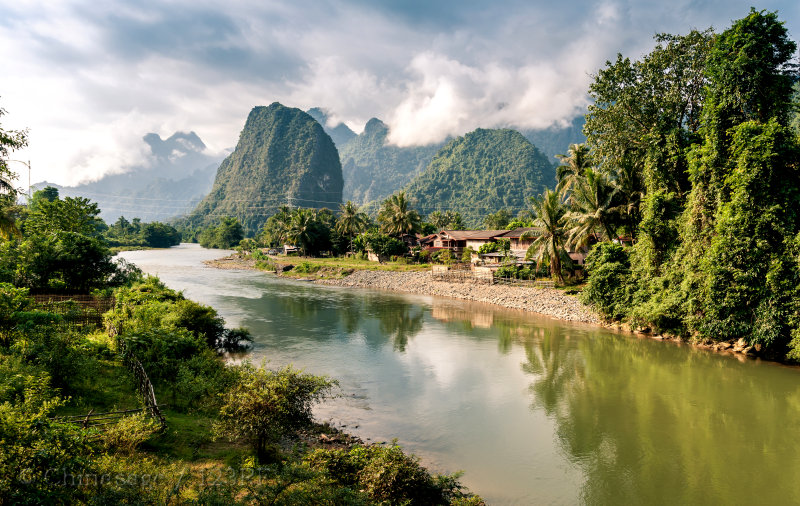
Myanmar / Burma 缅甸 (Miandian)
Population 51 million Area 676,578 sqkms GDP $4,751China's border with Myanmar/Burma is with the province of Yunnan. It roughly follows the edge of the high mountains but the line does not follow a distinct geographical feature. With the expansion of China's influence under the Qing dynasty Burma was forced to accept Chinese control and became a vassal state of China. Emperor Qianlong launched a number of campaigns to try to gain control of Burma's jade mines (jade had become the Emperor's fixation). In 1876 Britain devised plans of building a railway from India via Burma into China to eventually link with its burgeoning treaty port at Shanghai. Captain Margery ➚ who led the survey was murdered by the Chinese and the project abandoned. However British interest in protecting its Indian empire led to the conquest of Myanmar in 1886.
Burma, as part of the British Empire, was on the supply route into China during the Second World War. The Burma Road was the principal over-land route for supplies to the Nationalist capital at Chongqing. It was built with the aid of 200,000 Chinese laborers. The road transport was brought to a halt with the Japanese invasion of Myanmar in April 1942. A second route through Ledo ➚ re-established the link through northern Myanmar. American and British trained Chinese forces led a fearsome attack against the Japanese. By 1945 intensive jungle warfare by the allies drove the Japanese out of Myanmar.
Myanmar has been China's key ally against India in the region since liberation. Trade between the nations is now extensive with several roads crossing China's southern border.
See also Burma (Wikipedia) ➚India 印度 (Yindu)
Population 1,210 million Area 3,287,590 sqkms GDP $6,266The Himalayas form the most formidable natural boundary between any two countries in the world. The highest Himalayan peaks including Everest are dotted along the border. For many centuries the Chinese thought of India as an enchanted land beyond the mountains. It was from India that Buddhism came to China and Buddhism had a very deep and lasting effect on Chinese culture and philosophy. When India came under British control (c. 1770-1947), Britain's attitude to China reflected wider global interests, especially in the 18th century. During the Second World War protection of Britain's Indian Empire was a significant factor in British strategy which included the defense of Burma.
When the Dalai Lama fled Tibet to India in 1950, he settled at Tezpur just East of the Bhutan border within sight of the Himalayas. Relations between China and India reached a state of war in 1962 (and conflict flared up again briefly in 2020 ➚). The dispute was over small portions of territory along the border: the Aksai Chin ➚ and the N.E.F.A (North East Frontier Area) near the Myanmar border. The historical border had been drawn by the British Raj and apparently agreed by the Tibetans but not the Chinese. India feared the incursion by Chinese troops would lead to an all out invasion of the whole country. China pulled back on 21st November 1962 and the de facto agreement was that China would hold the Aksai Chin and India hold the N.E.F.A.. This dispute pushed India into the USSR's sphere of influence as Russia was then hostile to China. In the past decade India's increasing economic power and growth rate has rivaled that of China. The two most populous nations on Earth with a common border are still not the best of friends.
See also India (Wikipedia) ➚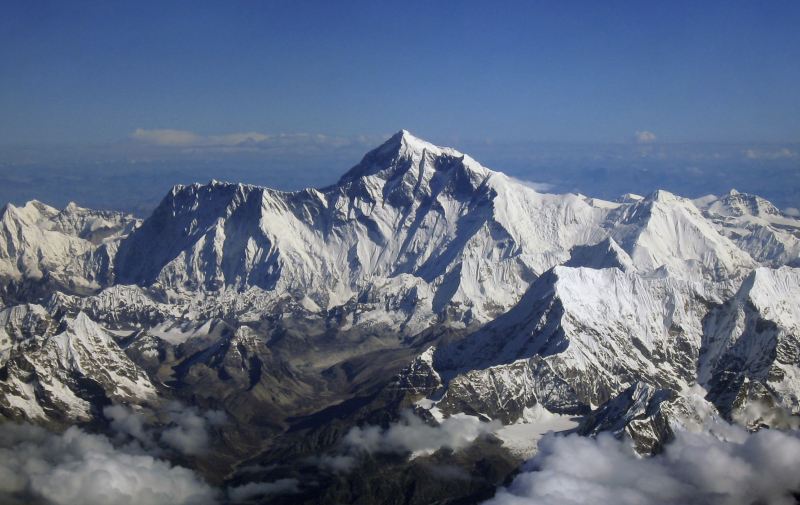
Nepal 尼泊尔 (Niboer)
Population 26 million Area 147,181 sqkms GDP $2,310Nestling in the Himalayas, the mountain kingdom of Nepal like Bhutan, has resisted control from both its neighbors India and China. Historically the birth of Siddhartha Gautama ➚ (Supreme Buddha) at Kapilavastu in 563BCE has had the greatest influence. Thereafter Buddhism has dominated the culture. After the fall of the Licchavi dynasty ➚ the area came under Tibetan control. The country has since showed loyalty to its Tibetan neighbors. The modern kingdom was founded by Prithvi Narayan Shah ➚ in 1768 and for a time Greater Nepal extended into northern India.
After the Nepal-Tibet-China War (1789-92) ended with Chinese victory, the modern border was fixed by the British, and although officially an independent kingdom it was effectively controlled by Britain. However the defeat of a British Army in the Anglo-Nepalese War (1815-16) led to admiration of the military effectiveness of the Nepalese Army, and native Nepalese Gurkhas ➚ serve in the U.K. army to the present day. The Maoist Communist Party ➚ of Nepal fought a Civil War (1996-2006) and the country is still seeking reconciliation. China, perhaps surprisingly, sided with the government rather than with the Maoist rebels.
See also Nepal (Wikipedia) ➚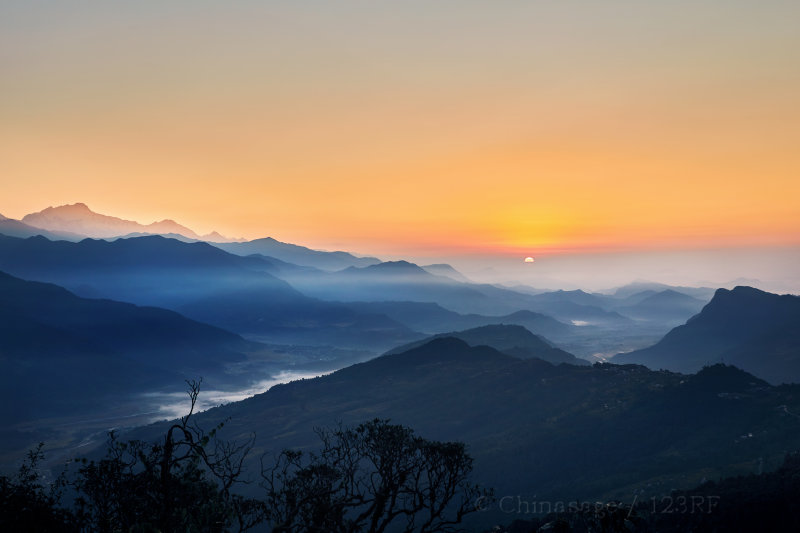
Bhutan 不丹 (Budan)
Population 1 million Area 38,394 sqkms GDP $6,112With a population of less than a million, the isolated mountainous kingdom of Bhutan has somehow managed to remain an independent nation. Details of early history are difficult to establish. Ugyen Wangchuck ➚ in the 1880s became the unifying influence after a Civil War. When his kingdom was recognized by the British in 1907, Bhutan achieved quasi-independent status. It was under British control, as a princely kingdom, up to 1947 when it became an independent nation. Buddhism is the principal religion of the peaceful people of Bhutan.
See also Bhutan (Wikipedia) ➚Pakistan 巴基斯坦 (Bajisitan)
Population 199 million Area 803,940 sqkms GDP $4,886China has a short 200 miles [322 kms] border with Pakistan in the Himalayas. The exact border is in dispute with India but also with China as it cuts through the politically volatile area of Kashmir ➚. As part of the Mughal Empire ➚ (1526-1857) Pakistan was run as a Muslim state by the descendents of Genghis Khan. Control of territory followed the Indus valley deep into Tibet.
On independence from Britain in 1947 ‘British India’ was split in three portions: West Pakistan (Muslim); India (Hindu) and East Pakistan (Muslim now Bangladesh). The border between Pakistan and India in the mountainous Kashmir district proved impossible to agree. There are major high passes through the mountains in this section : the Muztagh; Khunjerab and Karakoram Passes into Xinjiang province. Feeding on continued animosity with India, Pakistan sided with China in the Sino-Indian War of 1962. In the 1980s China helped arm Pakistan with weaponry including the atomic bomb. China and Pakistan are planning to build a major transportation link that would allow Chinese goods to rapidly reach an Indian Ocean port. It maintains good relations with China.
See also Pakistan (Wikipedia) ➚
Afghanistan 阿富汗 (Afuhan)
Population 32 million Area 652,864 sqkms GDP $1,777The border with Afghanistan is tiny, only 40 miles [64 kms] and is a geographical and a historical curiosity. The protrusion of the Afghan border towards China follows one valley - the Wakhan Valley ➚ of the Pamir River. Although historically the valley was a trade route, there is no maintained road at present. It served the purpose of denying Russia a direct border with British India. When Afghanistan was occupied by Soviet forces (1979-1992) hostility between Russia and China were reflected in the status of the puppet regime at Kabul. The current Afghan government has friendly relations with Beijing.
See also Afghanistan (Wikipedia) ➚Tajikistan 塔吉克斯坦 (Tajikesitan)
Population 8 million Area 143,100 sqkms GDP $2,247Like Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan was carved out of the fragments of the USSR in 1991. It is a relatively small and poor Central Asian nation.
Contacts with China go back to Han dynasty times under Emperor Wudi when Tajikistan was part of Bactria (known as 大夏 Dà xià by the Chinese). It has a short (200 miles [322 kms] border with Xinjiang province. The Tajik people have a distinctive culture and language and are a part of the Persian/Iranian family of peoples. There are sizable minorities of Russians and Uzbeks in Tajikistan while on the Chinese side of the border there are also many Tajik people.
See also Tajikistan (Wikipedia) ➚Kyrgyzstan 吉尔吉斯斯坦 (Jierjisisitan)
Population 6 million Area 199,951 sqkms GDP $2,372Kyrgyzstan is an independent Central Asian state formed when the USSR dissolved in 1991. In the 8th century the Kyrgyz culture and language developed around the Pamir Mountains. For centuries Issyk Kul Lake ➚ was a stop off on the Silk Road. It forms the northern border of most of Xinjiang province for about 500 miles [805 kms]. It remains a relatively poor nation of 5.5 million people. There is now a major road link to Kashgar in Xinjiang over the Turugart Pass ➚. There are many ethnic Kyrgyz people in Xinjiang province.
See also Kyrgyzstan (Wikipedia) ➚
Kazakhstan 哈萨克斯坦 (Hasekesitan)
Population 18 million Area 2,724,900 sqkms GDP $24,143The Kazakh culture developed among the Turkic tribes along the Silk Route in the 15th century. It came under Russian influence in the 18th century and part of the Russian Empire during the 19th. Kazakhstan is a large country covering an area similar to India; it has an 800 miles [1,287 kms] border with Xinjiang province. Many Kazakhs live in Xinjiang and they have tribal affinity with Kazakhstan, this probably makes it the biggest external threat to China. It was recognized in 1991 as an independent nation when the Soviet Union broke up. It now has a market economy with extensive oil and gas reserves.
See also Kazakhstan (Wikipedia) ➚

Japan 日本 (Rìběn)
Population 126 million Area 377,944 sqkms GDP $38,216Although Japan is an island nation with no land borders, Japan's relations with China has been important for centuries particularly in the last hundred years and so we have therefore dedicated a whole section on Chinese relations with Japan.
See also Japan (Wikipedia) ➚Taiwan 台湾 (Táiwān)
 Population 23 million Area 36,193 sqkms GDP $43,599
Population 23 million Area 36,193 sqkms GDP $43,599
The island of Taiwan (or Formosa or Chinese Taipei) is claimed by mainland China as a province. To reflect its eventful and contentious history we have a Taiwan section.
See also Taiwan (Wikipedia) ➚Philippines 菲律宾 (Fēilǜbīn)
 Population 101 million Area 300,000 sqkms GDP $7,412
Population 101 million Area 300,000 sqkms GDP $7,412
The archipelago of the Philippines is a fairly distant neighbor but reflecting its continuing strategic position between the US and China we have written a Philippines section to describe the islands.
See also Philippines (Wikipedia) ➚China and its Neighboring countries compared
Click on a column heading to sort the entries by that attribute.
| Country | Population | Area | Density | GDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afghanistan | 32 | 653 | 49 | 1,777 |
| Bhutan | 1 | 38 | 19 | 6,112 |
| Burma | 51 | 677 | 76 | 4,751 |
| China | 1,418 | 9,597 | 148 | 13,801 |
| India | 1,210 | 3,288 | 368 | 6,266 |
| Japan | 126 | 378 | 335 | 38,216 |
| Kazakhstan | 18 | 2,725 | 7 | 24,143 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 6 | 200 | 29 | 2,372 |
| Laos | 7 | 237 | 29 | 3,100 |
| Mongolia | 3 | 1,566 | 2 | 9,293 |
| Nepal | 26 | 147 | 180 | 2,310 |
| North Korea | 25 | 121 | 207 | 1,800 |
| Pakistan | 199 | 804 | 248 | 4,886 |
| Philippines | 101 | 300 | 335 | 7,412 |
| Russia | 144 | 17,098 | 8 | 8,184 |
| South Korea | 51 | 100 | 512 | 36,601 |
| Taiwan | 23 | 36 | 646 | 43,599 |
| Tajikistan | 8 | 143 | 57 | 2,247 |
| Vietnam | 91 | 339 | 268 | 5,621 |
Key: Estimated Population in millions (2014); Land area in units of 1000 sq. kms; Density in people per sq. km.; GDP Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita in dollars (using PPP measure).